
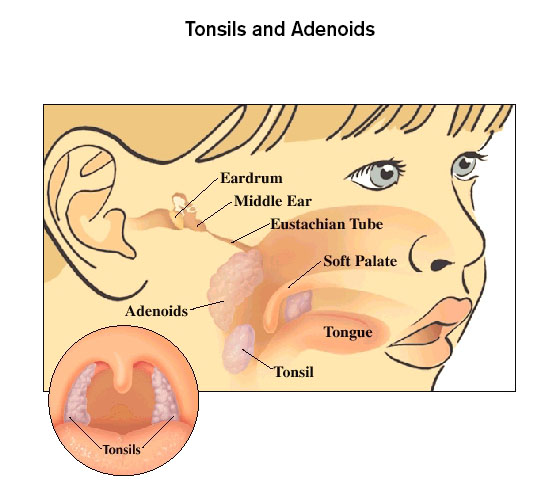
Everyone hates it when young children fall ill. Small children cannot tell what’s troubling them; they cry a lot, stop eating, and with coughs and colds, they vomit while coughing. As shown in the figure above, the ear, nose, and throat are connected, so ENT problems are interrelated.
Coughs, colds are at a peak when children interact with other children in the play group, at the age of 3-5 years. As they grow older, their immunity builds up and they fall less sick. The following are common problems in small children:
Respiratory Viral infections
Common cold viruses, flu viruses, measles, chicken pox, mumps, etc. These make the child sick and prone to allergies.
Do vaccinate your child, especially in tropical countries, to protect them from deadly diseases and their consequences.

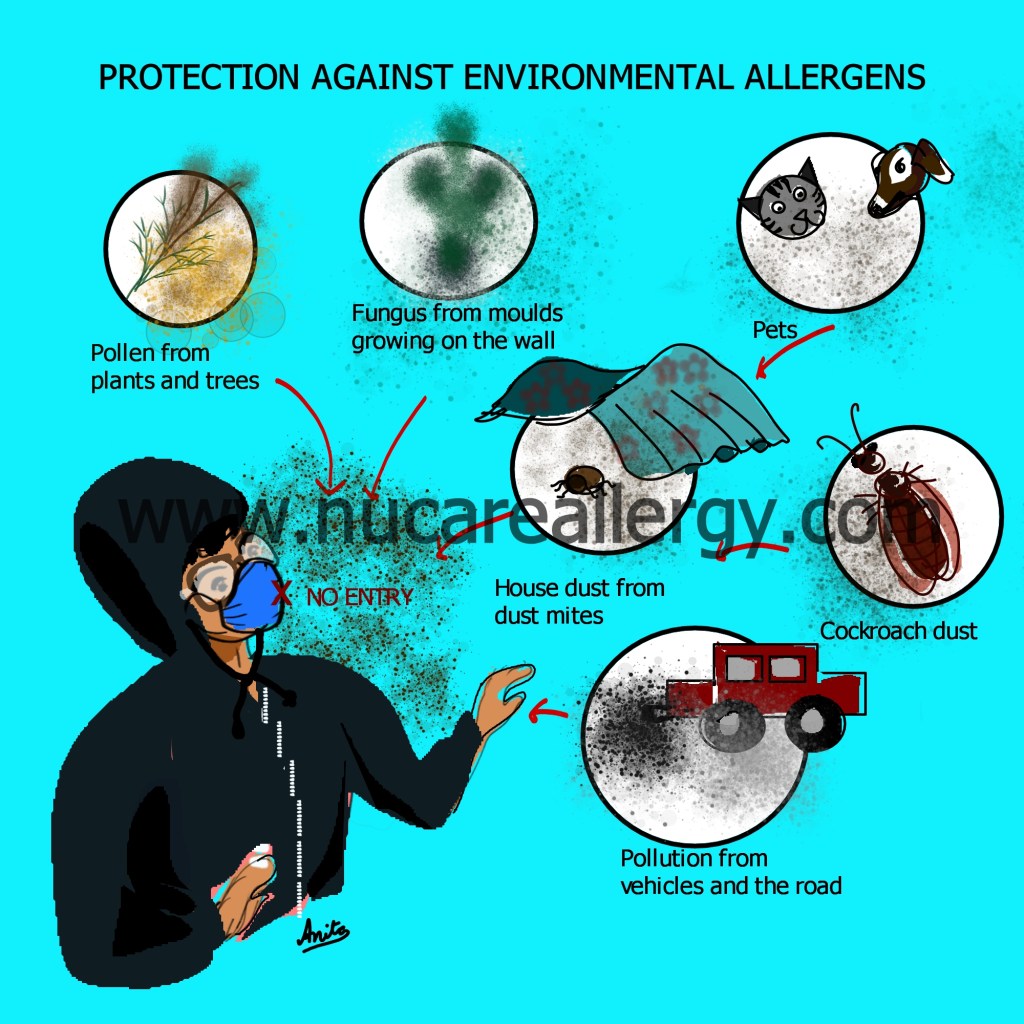
Allergies
Allergies to dust, pollen, fungi, pets and various foods are present
Food allergies are more common in children, such as milk, peanut, egg, wheat, tree nuts, soy, and seafood. These have to be identified as soon as possible, and avoidance measures should be followed
The Child should have an Epi-pen ready for prompt use in case of a food allergy for an anaphylactic attack. The patient and the caregiver should be instructed in the proper injection of deep intramuscular adrenaline to avoid complications
( Please refer to the previous blogs on allergies)

Adenoids and Tonsils


Infections of the tonsils and adenoids are very common in small children. The tonsils and adenoids are protective mechanisms of the body and help prevent spread of infection to the rest of the body. After the age of 5-7 years, the frequency of infections will go down and the tonsils and adenoids should become small in size
However, tonsils and adenoids become cause of concern if,
- The child has repeated severe infections at least once a month.
- The tonsils and adenoids are so huge that the child finds it difficult to breath especially during sleep.(childhood sleep apnea)
- Tonsillar infection and blocked nose persist after 7 years of age.
- Blood investigations like complete blood count and ASO titre are altered, showing beta hemolytic streptococci present in the body, leading to a risk of rheumatic heart disease
- Enlarged adenoids lead to chronic mouth breathing if untreated at the proper time. This affects the development of the face leading to typical ‘adenoid face’ , mouth open, the cheek bones don’t grow as they should leading to flattening of the face, high arched roof of the mouth and dental problems
The misconception is that children will ‘outgrow’ these infections, and so sometimes surgery is delayed, prolonging the suffering. If the child is very sick, it is advisable to go for adenotonsillectomy due to the following reasons:
- Infected tonsils and adenoids carry a lot of bacteria. They no longer can ‘protect’ the body. In fact they become more dangerous as infection from them can spread to the body and can lead to complications like rheumatic heart disease
- The cosmetic appearance of the face is changed
- They lead to sleeping disorders, paediatric sleep apnoea, and affect school performance and sports activity
Tonsils and adenoids can be removed by Coblator surgery. The coblator is a plasma wand, and at near normal temperature, tissue is ablated with minimal bleeding.

Adenoids are no longer scraped out like as was done earlier. This was a blind procedure and remnants used to cause adenoids to regrow. The surgery is done by visualizing the adenoids with an angled endoscope which is either inserted through the nose or through the mouth after pulling the palate back. They are removed under vision, leading to a complete removal and no recurrence.
Otitis Media
Frequent colds lead to fluid build up in the middle ear.
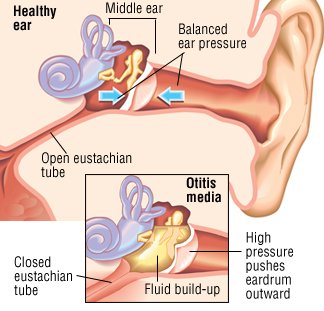
Acute Otitis media is frequent in small children as the tube connecting the ear and the throat is more horizontal and wider and opens up easily leading to more fluid collection
Smaller children cannot tell what is wrong.
- They keep on crying and may or may not clutch their ear. The pain is relieved with proper antibiotics and decongestant medications.
- In extreme cases the fluid , sometimes bloody, comes out through a small pinpoint hole in the ear drum and the pain is relieved.
- This is a relief since the pus can even reach the brain and other structures, if this does not happen
Chronic otitis media or otitis media with effusion.

- In some cases, especially small children with chronic allergies, there is a collection of clear fluid behind the ear drum, leading to difficulty in hearing. This fluid should subside with treatment for 2 or more months.
- In extreme cases a grommet or a ventilation tube is placed for the fluid to drain off. This grommet extrudes itself within a year or can be removed easily by the ENT doctor.
Discharging Ear
Sometimes pus coming from the ear does not dry completely. With frequent colds and infections a hole in the ear drum forms. This is common with flu, chicken pox, and measles or similar viral infections.
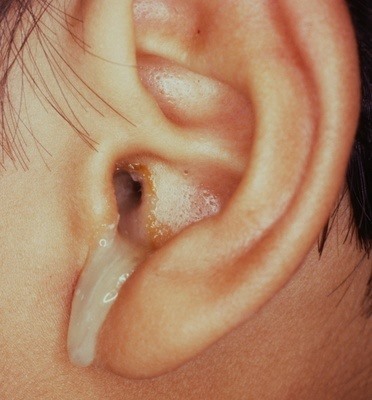

- In chronic cases a pus culture/ sensitivity is done to determine the organism and to start the proper antibiotic. In case of hole in the ear drum Tympanoplasty surgery is advisable.
- Surgery in young adults and at an earlier age is more successful because as time goes by, the bones of hearing become stiff, scar tissue forms and healing is affected.
Cholesteatoma
If coughs and colds persist for a long time, part of the ear drum gets pulled inside due to vacuum. This skin of the ear drum forms a pouch which starts expanding and growing inside the bone of the middle ear known as the mastoid cavity. This is called a cholesteatoma.
Cholesteatomas can also be present at birth. These are formed by small ‘pearls’ or sacs of skin embedded in the mastoid bone. As the child grows, these pearls grow too and expand, and cause infection in the middle ear.


Cholesteatomas don’t get better with medicine alone. If untreated they can reach the brain, the organs of balance and the facial nerve, the nerve which deals with movement of the face. In extreme cases the hearing of the ear is already damaged.
The child has to be operated. The disease is completely removed from the middle ear and the bone, with care taken to preserve important structures.
The above article is for information only. Please contact your doctor for expert advice and managment
Leave a reply to allergy care Cancel reply